lombok是一个编译级别的插件,它可以在项目编译的时候生成一些代码。在很多工具类的项目中都有这个功能。比如dagger。getter settter等代码。我们自然可以通过编译器比如IDEA的Generate生成,为啥要用这个?
说明 在项目开发阶段,一个class的属性是一直变化的,今天可能增加一个字段,明天可能删除一个字段。每次变化都需要修改对应的模板代码。另外,有的class的字段超级多,多到一眼看不完。如果加上模板代码,更难一眼看出来。更有甚者,由于字段太多,想要使用builder来创建。手动创建builder和字段和原来的类夹杂在一起,看起来真的难受。lombok的@Builder即可解决这个问题。
引入 引入就是加入lombok的jar包。
在maven中 直接加入依赖
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.projectlombok</groupId > <artifactId > lombok</artifactId > <version > 1.16.20</version > </dependency >
在gradle中 这里比较麻烦,需要添加一个编译时生成代码的插件。gradle里有几个这样的插件。但为了简化过程,lombok提供了新插件。
来源:官网 , github
首先,添加一个plugin
1 2 3 plugins { id 'io.franzbecker.gradle-lombok' version '1.11' }
然后,就可以了。还可以配置lombok的版本:
1 2 3 4 lombok { // optional: values below are the defaults version = "1.16.20" sha256 = "" }
IntelIJ IDEA 插件 在IDEA里使用需要添加一个插件。在插件里搜索lombok,安装,重启。
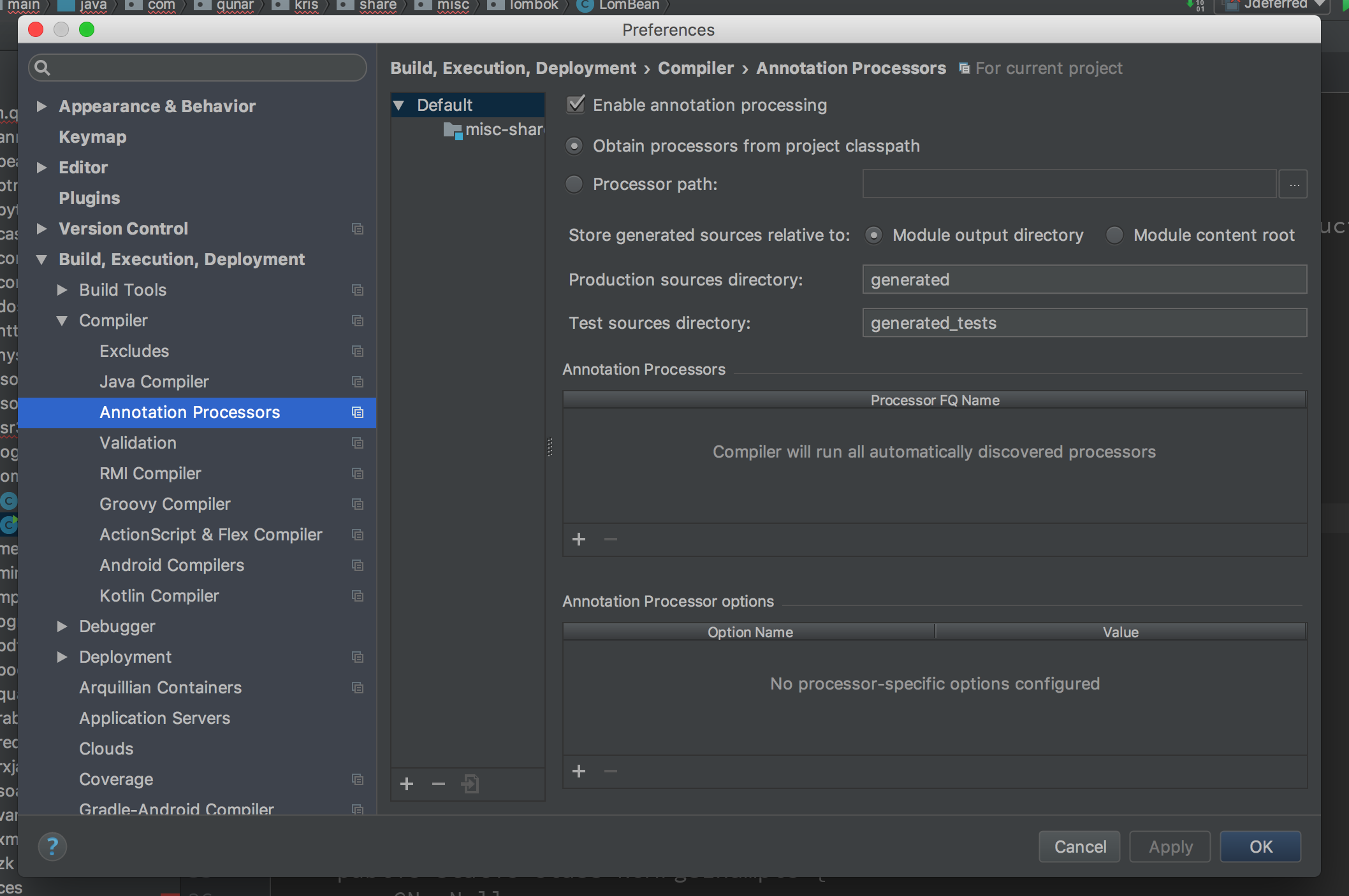
IDEA里需要在设置中启用annotation processors。
如果升级了InteliJ IDEA, 可能出现lombok不能用了,右键更新lombok plugin,重启即可。
基本用法 测试代码: https://github.com/Ryan-Miao/someTest/tree/master/src/main/java/com/test/lombok
Geter Setter 最简单的,最常用的,最直观的使用就是getter setter方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 package com.test.lombok;import lombok.AccessLevel;import lombok.Getter;import lombok.Setter;import java.util.Date;public class GetterSetterExample { @Getter @Setter private int age = 10 ; @Getter @Setter private boolean active; @Getter @Setter private Boolean none; @Getter @Setter private Date date; @Setter(AccessLevel.PROTECTED) private String name; @Override public String toString () { return String.format("%s (age: %d)" , name, age); } public static void main (String[] args) { GetterSetterExample example = new GetterSetterExample (); example.setActive(true ); example.setAge(123 ); example.setDate(new Date ()); example.setName("abc" ); example.setNone(false ); Date date = example.getDate(); Boolean none = example.getNone(); boolean active = example.isActive(); } }
简单使用没有问题,深入一点可以看到有些特殊设定。比如javadoc.
Getter声明创建getter方法;Setter声明创建setter方法;@Setter(AccessLevel.PROTECTED)可以添加参数,指定权限为私有;Attention!关于boolean的set前缀都是set,但getter不同,小写的boolean,即基本类型,前缀是is; Boolean,即包装类型,前缀是get;
编译后的结果如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 package com.test.lombok;import java.util.Date;public class GetterSetterExample { private int age = 10 ; private boolean active; private Boolean none; private Date date; private String name; public GetterSetterExample () { } public String toString () { return String.format("%s (age: %d)" , this .name, this .age); } public static void main (String[] args) { GetterSetterExample example = new GetterSetterExample (); example.setActive(true ); example.setAge(123 ); example.setDate(new Date ()); example.setName("abc" ); example.setNone(false ); Date date = example.getDate(); Boolean none = example.getNone(); boolean active = example.isActive(); } public int getAge () { return this .age; } public void setAge (int age) { this .age = age; } public boolean isActive () { return this .active; } public void setActive (boolean active) { this .active = active; } public Boolean getNone () { return this .none; } public void setNone (Boolean none) { this .none = none; } public Date getDate () { return this .date; } public void setDate (Date date) { this .date = date; } protected void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } }
ToString 虽然ToString在生产环境貌似没什么卵用。但是,很多情况下,我们还是需要这个的。因为记log。不想每次看log的时候是一串@地址,那就好好把toString()加上。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 package com.test.lombok;import lombok.Setter;import lombok.ToString;@Setter @ToString(exclude="id") public class ToStringExample { private static final int STATIC_VAR = 10 ; private String name; private Shape shape = new Square (5 , 10 ); private String[] tags; private int id; @ToString(callSuper=true, includeFieldNames=true) public static class Square extends Shape { private final int width, height; public Square (int width, int height) { this .width = width; this .height = height; } } @ToString public static class Shape { private int color; } public static void main (String[] args) { final ToStringExample example = new ToStringExample (); example.setId(1 ); example.setName("abc" ); example.setTags(new String []{"a" ,"b" ,"c" }); final Shape shape = new Square (1 ,2 ); example.setShape(shape); System.out.println(example.toString()); } }
1.@ToString最简单使用即可
打印结果如下:
ToStringExample(name=abc, shape=ToStringExample.Square(super=ToStringExample.Shape(color=0), width=1, height=2), tags=[a, b, c])
编译后的代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 package com.test.lombok;import java.util.Arrays;public class ToStringExample { private static final int STATIC_VAR = 10 ; private String name; private ToStringExample.Shape shape = new ToStringExample .Square(5 , 10 ); private String[] tags; private int id; public ToStringExample () { } public static void main (String[] args) { ToStringExample example = new ToStringExample (); example.setId(1 ); example.setName("abc" ); example.setTags(new String []{"a" , "b" , "c" }); ToStringExample.Shape shape = new ToStringExample .Square(1 , 2 ); example.setShape(shape); System.out.println(example.toString()); } public void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } public void setShape (ToStringExample.Shape shape) { this .shape = shape; } public void setTags (String[] tags) { this .tags = tags; } public void setId (int id) { this .id = id; } public String toString () { return "ToStringExample(name=" + this .name + ", shape=" + this .shape + ", tags=" + Arrays.deepToString(this .tags) + ")" ; } public static class Shape { private int color; public Shape () { } public String toString () { return "ToStringExample.Shape(color=" + this .color + ")" ; } } public static class Square extends ToStringExample .Shape { private final int width; private final int height; public Square (int width, int height) { this .width = width; this .height = height; } public String toString () { return "ToStringExample.Square(super=" + super .toString() + ", width=" + this .width + ", height=" + this .height + ")" ; } } }
@EqualsAndHashCode equals()和hashCode()在Java中有着举足轻重的基地作用,虽然通常很少关注。但是,这个必须不可省。不知道有几个可以手写出来的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 package com.test.lombok;import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;@EqualsAndHashCode(exclude={"id", "shape"}) public class EqualsAndHashCodeExample { private transient int transientVar = 10 ; private String name; private double score; private ToStringExample.Shape shape = new Square (5 , 10 ); private String[] tags; private int id; public String getName () { return this .name; } @EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper=true) public static class Square extends ToStringExample .Shape { private final int width, height; public Square (int width, int height) { this .width = width; this .height = height; } } public static void main (String[] args) { EqualsAndHashCodeExample example = new EqualsAndHashCodeExample (); EqualsAndHashCodeExample example1 = new EqualsAndHashCodeExample (); boolean equals = example.equals(example1); boolean b = example.canEqual(example); int i = example.hashCode(); } }
编译后的结果为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 package com.test.lombok;import com.test.lombok.ToStringExample.Shape;import java.util.Arrays;public class EqualsAndHashCodeExample { private transient int transientVar = 10 ; private String name; private double score; private Shape shape = new EqualsAndHashCodeExample .Square(5 , 10 ); private String[] tags; private int id; public EqualsAndHashCodeExample () { } public String getName () { return this .name; } public static void main (String[] args) { EqualsAndHashCodeExample example = new EqualsAndHashCodeExample (); EqualsAndHashCodeExample example1 = new EqualsAndHashCodeExample (); example.equals(example1); boolean b = example.canEqual(example); int i = example.hashCode(); } public boolean equals (Object o) { if (o == this ) { return true ; } else if (!(o instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample)) { return false ; } else { EqualsAndHashCodeExample other = (EqualsAndHashCodeExample)o; if (!other.canEqual(this )) { return false ; } else { label31: { Object this$name = this .getName(); Object other$name = other.getName(); if (this $name == null ) { if (other$name == null ) { break label31; } } else if (this $name.equals(other$name)) { break label31; } return false ; } if (Double.compare(this .score, other.score) != 0 ) { return false ; } else { return Arrays.deepEquals(this .tags, other.tags); } } } } protected boolean canEqual (Object other) { return other instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample; } public int hashCode () { int PRIME = true ; int result = 1 ; Object $name = this .getName(); int result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode()); long $score = Double.doubleToLongBits(this .score); result = result * 59 + (int )($score >>> 32 ^ $score); result = result * 59 + Arrays.deepHashCode(this .tags); return result; } public static class Square extends Shape { private final int width; private final int height; public Square (int width, int height) { this .width = width; this .height = height; } public boolean equals (Object o) { if (o == this ) { return true ; } else if (!(o instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample.Square)) { return false ; } else { EqualsAndHashCodeExample.Square other = (EqualsAndHashCodeExample.Square)o; if (!other.canEqual(this )) { return false ; } else if (!super .equals(o)) { return false ; } else if (this .width != other.width) { return false ; } else { return this .height == other.height; } } } protected boolean canEqual (Object other) { return other instanceof EqualsAndHashCodeExample.Square; } public int hashCode () { int PRIME = true ; int result = super .hashCode(); result = result * 59 + this .width; result = result * 59 + this .height; return result; } } }
构造函数@NoArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor, @AllArgsConstructor Java中class的一切起源于构造器。大家最喜欢的还是构造函数创建对象。这里有一点比较坑的是无参构造函数。当你自己添加一个带有参数的构造函数后,无参构造函数则别隐藏。通常也没啥问题,但当你使用jackson反序列化对象的时候就被恶心到了。jackson通过无参构造函数创建对象。因此,当你考虑这个class会用来序列化为json的时候,即必须手动添加一个无参数构造函数。
@NoArgsConstructor 当你想要创建一个valueobject,DDD中的值对象,要求实现Immutable,那么无参数构造器就不合适了。@NoArgsConstructor会生成一个空的构造器。如果你设置了final field,那么编译会报错。如果你强制执行创建无参数构造器。即,@NoArgsConstructor(force = true),那么final的field会初始化为0/false/null。通常适合与@Data集成。
1 2 3 4 @NoArgsConstructor public static class NoArgsExample { @NonNull private String field; }
最终生成代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public static class NoArgsExample { @NonNull private String field; public NoArgsExample () { } }
对于final的字段,我认为我不会用空构造器来做这件事。所以,感觉这个参数force=true不要也罢,鸡肋。
@RequiredArgsConstructor 一个class可以有很多属性,但你可能只关心其中的几个字段,那么可以使用@RequiredArgsConstructor。@NonNull将标注这个字段不应为null,初始化的时候会检查是否为空,否则抛出NullPointException。在上面的无参构造函数中被忽略了。那么,对于关注的字段标注@NonNull, @RequiredArgsConstructor则会生成带有这些字段的构造器。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @RequiredArgsConstructor public class RequiredArgsExample { @NonNull private String field; private Date date; private Integer integer; private int i; private boolean b; private Boolean aBoolean; }
最终生成结果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class RequiredArgsExample { @NonNull private String field; private Date date; private Integer integer; private int i; private boolean b; private Boolean aBoolean; public RequiredArgsExample (@NonNull String field) { if (field == null ) { throw new NullPointerException ("field" ); } else { this .field = field; } } }
只有@NonNull会生成构造器。其他默认,Java的class初始化默认为null.false,0.
lombok提供了另一种初始化做法,静态初始化。即私有构造器,使用静态方法创建对象。这种做法看起来简单,但通常用的不多。因为静态初始化的东西很难mock,对测试不够友好。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "of") public static class RequiredArgsStaticExample { @NonNull private String field; private Date date; private Integer integer; private int i; private boolean b; private Boolean aBoolean; }
最终生成代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class ConstructorExample <T> { private int x; private int y; @NonNull private T description; private ConstructorExample (@NonNull T description) { if (description == null ) { throw new NullPointerException ("description" ); } else { this .description = description; } } public static <T> ConstructorExample<T> of (@NonNull T description) { return new ConstructorExample (description); } }
@AllArgsConstructor 想要初始化所有字段。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED) public class ConstructorExample <T> { private int x, y; @NonNull private T description; }
最终生成代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class ConstructorExample <T> { private int x; private int y; @NonNull private T description; protected ConstructorExample (int x, int y, @NonNull T description) { if (description == null ) { throw new NullPointerException ("description" ); } else { this .x = x; this .y = y; this .description = description; } } }
必用项@Data 1 @Data`是一个集合体。包含`Getter`,`Setter`,`RequiredArgsConstructor`,`ToString`,`EqualsAndHashCode
不可变对象valueobject @Value 这个看起来很美好,就是可以帮忙生成一个不可变对象。对于所有的字段都将生成final的。但我感觉有点失控。注解的优势应该是所见即所得,可以通过字面量来传递消息。而@Value字段给字段加final会让人困惑,因为这更改了我们的定义。当我想声明一个Immutable对象的时候,我会显示的给字段加一个限定final。
同@Data, @Value是一个集合体。包含Getter,AllArgsConstructor,ToString,EqualsAndHashCode。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Value public class Room { @NonNull private String id; private String name; private boolean active; private Date createTime; }
编译后
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 public final class Room { @NonNull private final String id; private final String name; private final boolean active; private final Date createTime; public Room (@NonNull String id, String name, boolean active, Date createTime) { if (id == null ) { throw new NullPointerException ("id" ); } else { this .id = id; this .name = name; this .active = active; this .createTime = createTime; } } @NonNull public String getId () { return this .id; } public String getName () { return this .name; } public boolean isActive () { return this .active; } public Date getCreateTime () { return this .createTime; } public boolean equals (Object o) { if (o == this ) { return true ; } else if (!(o instanceof Room)) { return false ; } else { Room other = (Room)o; Object this$id = this .getId(); Object other$id = other.getId(); if (this $id == null ) { if (other$id != null ) { return false ; } } else if (!this $id.equals(other$id)) { return false ; } label41: { Object this$name = this .getName(); Object other$name = other.getName(); if (this $name == null ) { if (other$name == null ) { break label41; } } else if (this $name.equals(other$name)) { break label41; } return false ; } if (this .isActive() != other.isActive()) { return false ; } else { Object this$createTime = this .getCreateTime(); Object other$createTime = other.getCreateTime(); if (this $createTime == null ) { if (other$createTime != null ) { return false ; } } else if (!this $createTime.equals(other$createTime)) { return false ; } return true ; } } } public int hashCode () { int PRIME = true ; int result = 1 ; Object $id = this .getId(); int result = result * 59 + ($id == null ? 43 : $id.hashCode()); Object $name = this .getName(); result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode()); result = result * 59 + (this .isActive() ? 79 : 97 ); Object $createTime = this .getCreateTime(); result = result * 59 + ($createTime == null ? 43 : $createTime.hashCode()); return result; } public String toString () { return "Room(id=" + this .getId() + ", name=" + this .getName() + ", active=" + this .isActive() + ", createTime=" + this .getCreateTime() + ")" ; } }
最喜欢的项 @Builder 对于喜欢builder模式的人来说,声明式简化对象创建流程让一切看得美好。但是,手动复制字段,手动创建方法很让人不喜。@Builder解决了刚需。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 @Data @Builder(toBuilder = true) public class Room { @NonNull private String id; private String name; private boolean active; private Date createTime; @Singular private Set<String> occupations; public static void main (String[] args) { Room room = Room.builder().active(true ) .name("name" ) .id("id" ) .createTime(new Date ()) .occupation("1" ) .occupation("2" ) .build(); Assert.assertEquals(2 , room.getOccupations().size()); } }
这才是我们想要的建造者。对应生成的代码为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 package com.test.lombok;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.Date;import java.util.LinkedHashSet;import java.util.Set;import lombok.NonNull;import org.junit.Assert;public class Room { @NonNull private String id; private String name; private boolean active; private Date createTime; private Set<String> occupations; public static void main (String[] args) { Room room = builder().active(true ).name("name" ).id("id" ).createTime(new Date ()).occupation("1" ).occupation("2" ).build(); Assert.assertEquals(2L , (long )room.getOccupations().size()); } Room(@NonNull String id, String name, boolean active, Date createTime, Set<String> occupations) { if (id == null ) { throw new NullPointerException ("id" ); } else { this .id = id; this .name = name; this .active = active; this .createTime = createTime; this .occupations = occupations; } } public static Room.RoomBuilder builder () { return new Room .RoomBuilder(); } public Room.RoomBuilder toBuilder () { return (new Room .RoomBuilder()).id(this .id).name(this .name).active(this .active).createTime(this .createTime).occupations(this .occupations); } @NonNull public String getId () { return this .id; } public String getName () { return this .name; } public boolean isActive () { return this .active; } public Date getCreateTime () { return this .createTime; } public Set<String> getOccupations () { return this .occupations; } public void setId (@NonNull String id) { if (id == null ) { throw new NullPointerException ("id" ); } else { this .id = id; } } public void setName (String name) { this .name = name; } public void setActive (boolean active) { this .active = active; } public void setCreateTime (Date createTime) { this .createTime = createTime; } public void setOccupations (Set<String> occupations) { this .occupations = occupations; } public boolean equals (Object o) { if (o == this ) { return true ; } else if (!(o instanceof Room)) { return false ; } else { Room other = (Room)o; if (!other.canEqual(this )) { return false ; } else { label63: { Object this$id = this .getId(); Object other$id = other.getId(); if (this $id == null ) { if (other$id == null ) { break label63; } } else if (this $id.equals(other$id)) { break label63; } return false ; } Object this$name = this .getName(); Object other$name = other.getName(); if (this $name == null ) { if (other$name != null ) { return false ; } } else if (!this $name.equals(other$name)) { return false ; } if (this .isActive() != other.isActive()) { return false ; } else { Object this$createTime = this .getCreateTime(); Object other$createTime = other.getCreateTime(); if (this $createTime == null ) { if (other$createTime != null ) { return false ; } } else if (!this $createTime.equals(other$createTime)) { return false ; } Object this$occupations = this .getOccupations(); Object other$occupations = other.getOccupations(); if (this $occupations == null ) { if (other$occupations != null ) { return false ; } } else if (!this $occupations.equals(other$occupations)) { return false ; } return true ; } } } } protected boolean canEqual (Object other) { return other instanceof Room; } public int hashCode () { int PRIME = true ; int result = 1 ; Object $id = this .getId(); int result = result * 59 + ($id == null ? 43 : $id.hashCode()); Object $name = this .getName(); result = result * 59 + ($name == null ? 43 : $name.hashCode()); result = result * 59 + (this .isActive() ? 79 : 97 ); Object $createTime = this .getCreateTime(); result = result * 59 + ($createTime == null ? 43 : $createTime.hashCode()); Object $occupations = this .getOccupations(); result = result * 59 + ($occupations == null ? 43 : $occupations.hashCode()); return result; } public String toString () { return "Room(id=" + this .getId() + ", name=" + this .getName() + ", active=" + this .isActive() + ", createTime=" + this .getCreateTime() + ", occupations=" + this .getOccupations() + ")" ; } public static class RoomBuilder { private String id; private String name; private boolean active; private Date createTime; private ArrayList<String> occupations; RoomBuilder() { } public Room.RoomBuilder id (String id) { this .id = id; return this ; } public Room.RoomBuilder name (String name) { this .name = name; return this ; } public Room.RoomBuilder active (boolean active) { this .active = active; return this ; } public Room.RoomBuilder createTime (Date createTime) { this .createTime = createTime; return this ; } public Room.RoomBuilder occupation (String occupation) { if (this .occupations == null ) { this .occupations = new ArrayList (); } this .occupations.add(occupation); return this ; } public Room.RoomBuilder occupations (Collection<? extends String> occupations) { if (this .occupations == null ) { this .occupations = new ArrayList (); } this .occupations.addAll(occupations); return this ; } public Room.RoomBuilder clearOccupations () { if (this .occupations != null ) { this .occupations.clear(); } return this ; } public Room build () { Set occupations; switch (this .occupations == null ? 0 : this .occupations.size()) { case 0 : occupations = Collections.emptySet(); break ; case 1 : occupations = Collections.singleton(this .occupations.get(0 )); break ; default : Set<String> occupations = new LinkedHashSet (this .occupations.size() < 1073741824 ? 1 + this .occupations.size() + (this .occupations.size() - 3 ) / 3 : 2147483647 ); occupations.addAll(this .occupations); occupations = Collections.unmodifiableSet(occupations); } return new Room (this .id, this .name, this .active, this .createTime, occupations); } public String toString () { return "Room.RoomBuilder(id=" + this .id + ", name=" + this .name + ", active=" + this .active + ", createTime=" + this .createTime + ", occupations=" + this .occupations + ")" ; } } }
总结 lombok还提供了其他几个注解,以及还有好多内置的参数没有讲解。但是,根据2-8原理,我们根本不需要。上面这几个足够了。更多的注解只会增加理解阅读难度。
参考 https://projectlombok.org/features/all http://kriszhang.com/lombok/
![]()